E
ffects
of
ozone
on
the
pain
and
disability
in
patients
with
failed
back
surgery
syndrome
R
ev
A
ssoc
M
ed
B
ras
2017; 63(4):355-360
357
R
esults
The patients’ ages ranged from 24 to 66 years (mean 46.1),
63.16% were male and 36.84% were female. Just under a
third had attended higher education. Half of the patients
were on leave from work because of pain, unemployment
or retirement. Smoking was reported by 21.1% and alco-
hol abuse by 10.5% of the patients. Associated diseases
included type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, fibromy-
algia and bipolar disorder. Other diseases such as tuber-
culosis, Hansen’s disease, Chagas disease and neoplasms
were not observed in the sample. The main diagnoses
associated with pain were radiculopathy (57.89%), followed
by low back and leg pain (36.84) and low back pain (5.26%).
In only three cases the pain was related to a history of
trauma to the lumbar spine. The mean time to onset of
pain was 12.5 years. More than one surgery was indicated
for the treatment of pain in 57.9%, and in 63.16% of the
cases lumbar spine arthrodesis was performed, without
significant pain improvement (Table 1).
TABLE 1
Clinical characteristics of patients.
Characteristic
n (%)
Mean age (SD)*
46.1 ± 10.7
Sex
Male
12 (63.16)
Female
7 (36.84)
Education
Primary and middle school
10 (52.63)
High school
4 (21.05)
Higher studies
5 (26.32)
Occupation
Homemaker
1 (5.26)
Active
5 (26.32)
On sick leave**
5 (26.32)
Retired
3 (15.79)
Unemployed
5 (26.32)
Comorbidities
Diabetes
3 (15.79)
Dyslipidemia
1 (5.26)
Fibromyalgia
2 (10.53)
Bipolar affective disorder
1 (5.26)
Habits
Alcohol abuse
2 (10.53)
Smoking
4 (21.05)
Trauma-related pain Yes
2 (10.53)
No
16 (84.21)
Site of pain
L5
14 (73.68)
L5 + S1
4 (21.05)
S1
1 (5.26)
Duration of pain
12.5 ± 6.5
Number of surgeries 1
8 (42.11)
2
6 (31.58)
≥ 3
5 (26.32)
(
continues
)
TABLE 1
(Cont.) Clinical characteristics of patients.
Characteristic
n (%)
Arthrodesis
Yes
12 (63.16)
No
7 (36.84)
Additional treatments Physiotherapy
19 (100)
Acupuncture
17 (89.47)
Trigger point deactivation 1 (5.26)
Psychotherapy
8 (42.11)
Previous epiduroscopy
4 (21.05)
*Mean age plus standard deviation (SD); **Patient on sick leave through the social secu-
rity system.
Of the 19 patients, 18 scored higher than or equal to 4
on the DN4 questionnaire, being diagnosed with neuro-
pathic pain. However, during clinical evaluation, we ob-
served that 17 patients had a mixed pain pattern, 12 with
predominantly neuropathic pain (PNP) and seven with
predominantly non-neuropathic pain (PNNP).
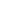
There was a mean reduction in the VAS scale from
8.47 to 7.05, which was statistically significant (Figure 1A).
There was a significant reduction in NPSI from 62.74 to
54.21 points (p=0.034). In the ODI assessment, no sig-
nificant improvement in disability was observed after the
procedure (p=0.217). A similar result was observed with
the Roland-Morris questionnaire, which obtained a mean
decrease from 14.47 to 13.84, although not statistically
significant (p=0.438). Functional impairment was also
evident in the BPI of the patients, since in the field that
assessed interference in daily activities there was a nonsig-
nificant reduction from 7.63 to 6.71. However, similarly
to VAS and NPSI, BPI showed a statistically significant
reduction in pain intensity from 7.68 to 6.58 (Table 2).
Comparing the results obtained in the PNP and PNNP
groups, no significant difference (p>0.05) was observed
in the postoperative reevaluation scores, both for VAS
(Figure 1B) and for the other scales.
D
iscussion
The first records of the use of ozone for medicinal pur-
poses date back to the early twentieth century during the
First World War. Its germicidal and analgesic effect was
observed in the treatment of post-traumatic gas gangrene
in German soldiers.
31
Currently, ozone used for therapeutic purposes is a
mixture of oxygen and ozone at 5%. The gas has a cell
oxidation and diffusion capacity ten times higher than
that of oxygen. These characteristics suggest that, when
ozone comes into contact with biologically active tissue,
it reacts with numerous organic molecules forming sev-