T
avares
RS
et
al
.
344
R
ev
A
ssoc
M
ed
B
ras
2017; 63(4):341-346
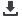
FIGURE 1
HbA1c comparison between control and heterozygous children.
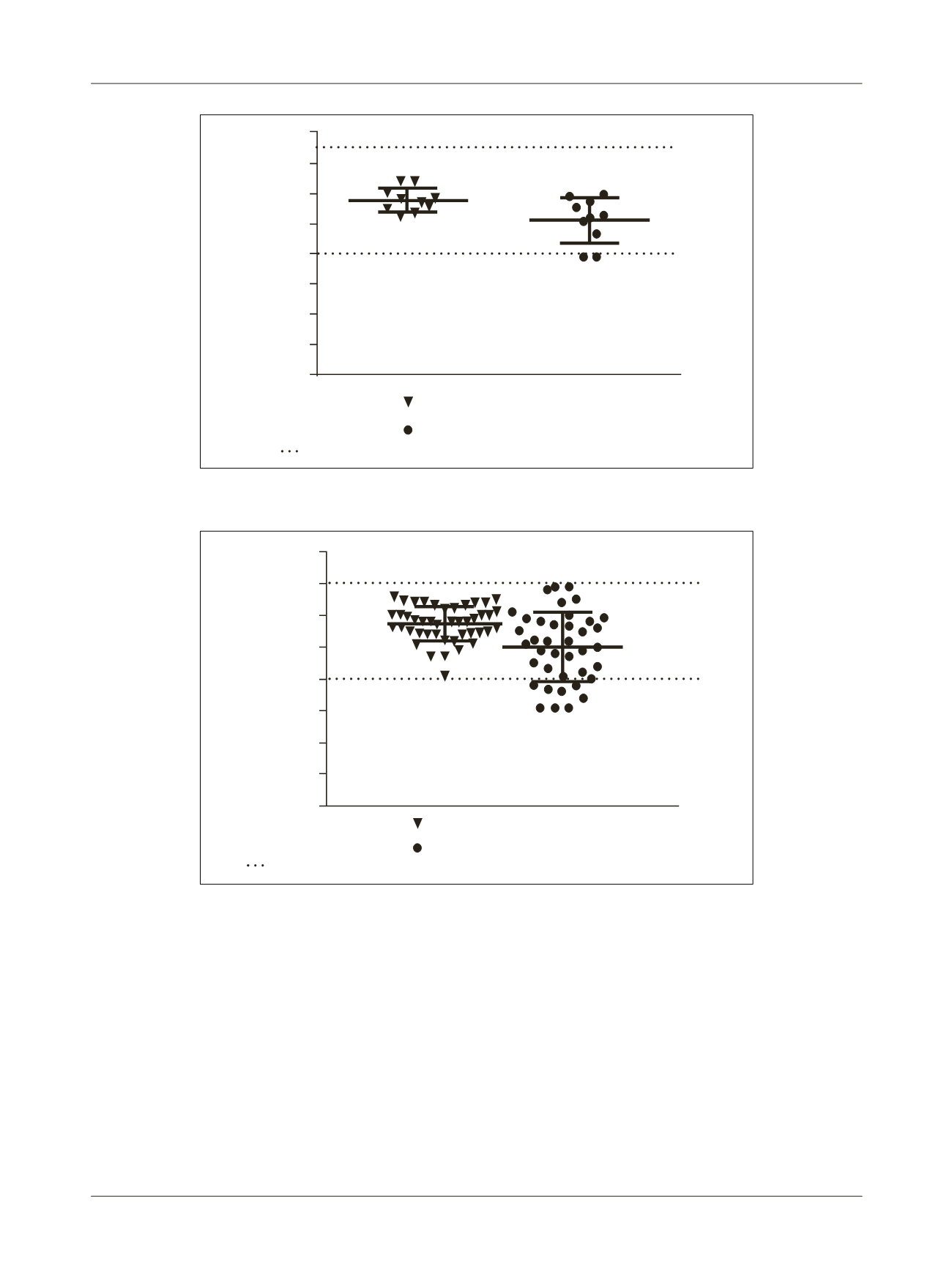
FIGURE 2
HbA1c comparison between control and heterozygous adults.
HbA1c Control
HbA1c Heterozygous
Reference range
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
%
HbA1c Control
HbA1c Heterozygous
Reference range
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
%
when the hemoglobin variant or its glycosylated form
cannot be separated from hemoglobin A or HbA1c.
23,24
In contrast, heterozygous hemoglobin S and C samples
did not affect the assay.
25
Not only hemoglobinopathies, including thalassemia
syndromes, but also factors that affect red blood cell sur-
vival, age, uremia, hyperbilirubinemia and iron deficiency
can affect the results of HbA1c tests. Racial and ethnic
differences, genetic variation in hemoglobin glycation and
assay methodology may also influence the results.
26
New methods are being developed, such as mass spec-
trometry, which is based on the suppression of fluores-
cence of a boron eosin in acid solution, and shows mini-
mal interference of the hemoglobin variants.
27-30
Despite
these valuable attributes, cost of equipment and complex-
ity of the operation limit its use.
31
According to studies, the presence of genetic variants
of hemoglobin under heterozygous conditions may interfere
with the measurement of HbA1c, resulting in falsely high
or decreased values, depending on the type of test used.