E
spíndula
RC
et
al
.
1008
R
ev
A
ssoc
M
ed
B
ras
2017; 63(11):1006-1011
A total of four studies
1,8,19,20
were included in the review.
The number of participants in each study ranged from 26
to 57. Two studies were fromTurkey, one from Iran and one
from the USA. The mean age of participants in each study
ranged from 44.11±6.19 to 56.50±12.97 years. Most stud-
ies included women diagnosed with stage I, II or III breast
cancer. Most of the studies prescribed pilates three times
per week during 8 weeks and each session lasted 45-60
minutes. All studies had supervision of a physiotherapist.
Methodological quality of included studies
We used the Risk of Bias tool adopted in Cochrane reviews
to analyze the risk of bias in randomized controlled trials.
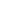
Figure 2 describes each category of bias assessed as low
risk, unclear risk and high risk. Random sequence gen-
eration was properly described only in two studies;
1,20
other two studies
8,19
did not provide enough information
about how randomization was conducted and were ran-
domized according to baseline values.
Allocation concealment was unclear in three stud-
ies,
1,8,19
which did not provide information on how it was
done. Alpozgen et al.
20
properly described allocation con-
cealment and did not conceal allocation. Blinding of
participants, personnel and outcome assessment pre-
sented high risk in all studies due to the characteristics
of participants; nevertheless, the outcome assessor could
have been blinded.
Two studies
1,19
had high loss of follow-up and did not
properly adjust the statistics for the missing participants,
while other two studies
8,19
did properly adjust the statisti-
cal analysis. All studies reported what they proposed in the
methods; however, most of them did not present a trial
registration number and thus we judged all studies as low
risk of bias for selective reporting. In the category Other
bias, one study was considered High risk, since the study
design was not adequate to answer the research question.
Pilates x home-based exercise
Only one comparison was possible in this study. After
extracting all data from the primary studies, we observed
that two studies
1,20
compared pilates x home-based exer-
cises for the outcome functional capacity. Both studies
used different scales to measure functional capacity, thus
we used standardized mean difference to pool the results.
Using random effects meta-analysis we found signi cant
difference between pilates x home-based exercise (two
studies, 79 participants; standardized mean difference
FIGURE 2
Results of the evaluation of each study according to the
Risk of Bias tool.
Random sequence generation (selection bias)
Allocation concealment (selection bias)
Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias)
Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias)
Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias)
Selective reporting (reporting bias)
Other biases
Azamian 2015
Eyigor 2010
Martin 2013
Zengin Alpozgen 2016
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
?
?
? ?
?
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ +
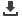
FIGURE 1
Flow chart of systematic review process.
34 records
identified through
database
searching
32 records after
duplicates removed
32 records
screened
11 full-text
articles assessed
for eligibility
7 full-text
articles excluded,
with reasons
4 studies included
in qualitative
synthesis
21 records
excluded
2 additional records
identified through
other sources