J
osé
BPS
et
al
.
608
R
ev
A
ssoc
M
ed
B
ras
2014; 60(6):599-612
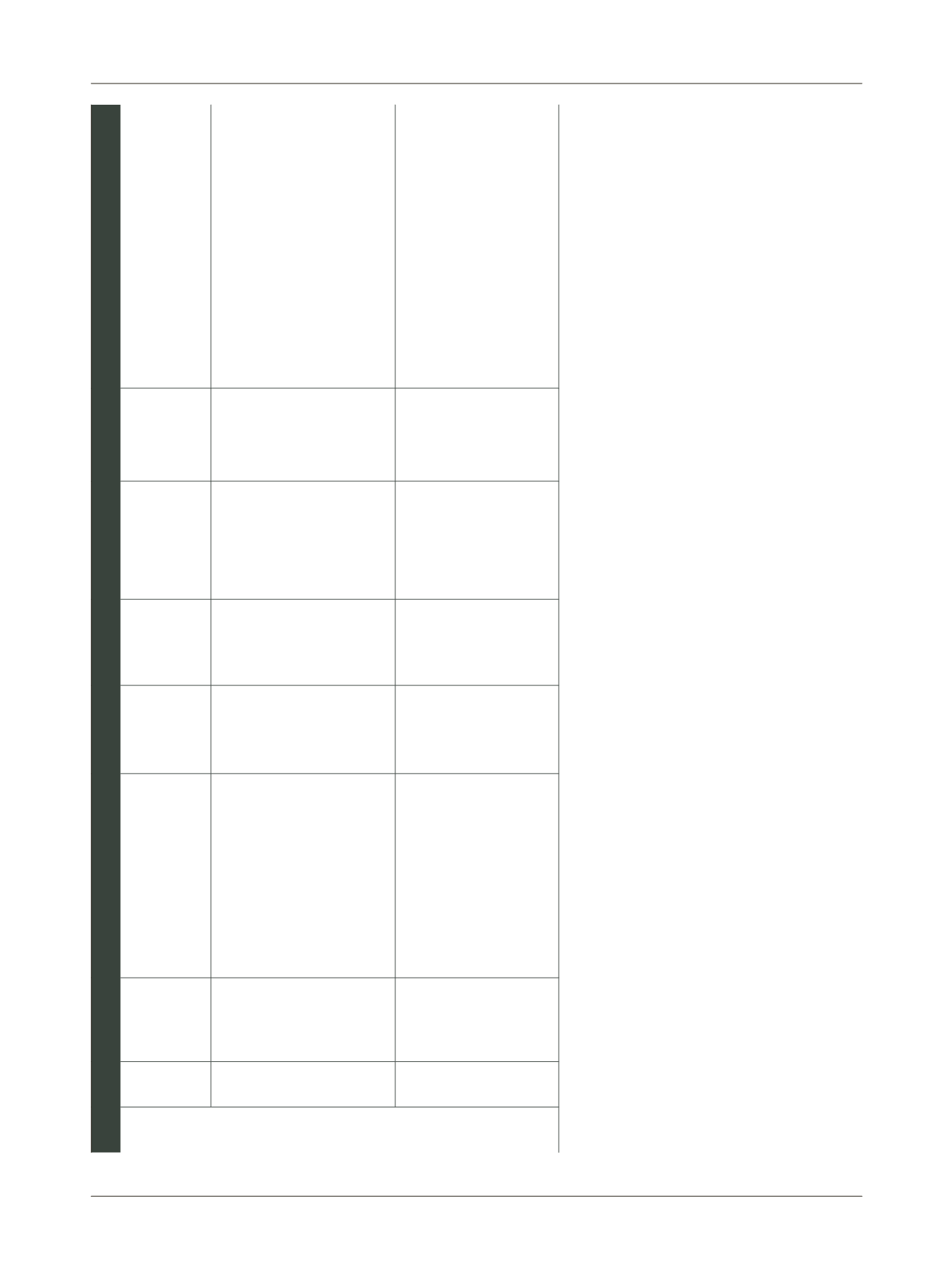
Table 1
Synopsis of the articles relating to acute respiratory tract infections (ARI), tuberculosis, asthma, COPD, and asthma and COPD in conjunction (continuation)
Asthma and COPD
37
Starren et al.,
2012, United
Kingdom
To check the operation of a unit of
reference for respiratory conditions
by reviewing the diagnoses of
referrals from GPs
Pulmonologists
Cross-
sectional
1,156; All age
groups; 61.3
28
Of the 1,156 patients referred, COPD was the most
common cause (445/666; 66.8%); over one third of
the diagnoses suggested by GPs were incorrect
(161/445; 36%)
38
Lucas et al.,
2012,
Netherlands
To assess what criteria GPs use to
justify their diagnostic hypothesis of
asthma and COPD; whether the
evaluations by experts cause
changes in diagnoses of GPs; and
whether to make GPs justify their
diagnostic hypotheses, influences
the diagnosis given in the reference
center
Pulmonologists
Cross-
sectional
284; 2-88; 51
17
Only 50% of diagnostic hypotheses were confirmed
by the specialized service. The chances of asthma
were confirmed more frequently (62%) than those
of COPD (40%). The justifications for the
diagnostic hypotheses of GPs did not influence the
results
39
Broekhuizen
et al., 2010,
Netherlands
To determine the frequency of
asthma or COPD in people aged
over 50 years who consult their GPs
because of persistent cough
Panel with an
experienced
GP and a
pulmonary
specialist
Cross-
sectional
353; ≥50; 63
73
After evaluation of pulmonary function tests and
discussion of clinical data by a panel of two
doctors, it was concluded that 29% of patients had
a diagnosis of COPD, 7% had asthma, and 4% were
diagnosed with mixed disease. It should be
reiterated that these diagnoses were new, that is,
they were not previous diagnoses made by assistant
GPs
1
Ref - Reference,
2
CRP - C-reactive Protein,
3
ROC - receiver operating characteristics curve,
4
ESR - Erythrocyte sedimentation rate,
5
PCT - Procalcitonin
6
AFB - Acid-fast bacilli,
7
GOLD -Global Initiative for Lung Chronic Obstructive,
8
FEV1 Forced expira-
tory volume in 1 second,
9
FVC- Forced vital capacity.