
C
urrent
clinical
approach
to
patients
with
disorders
of
consciousness
R
ev
A
ssoc
M
ed
B
ras
2016; 62(4):377-384
383
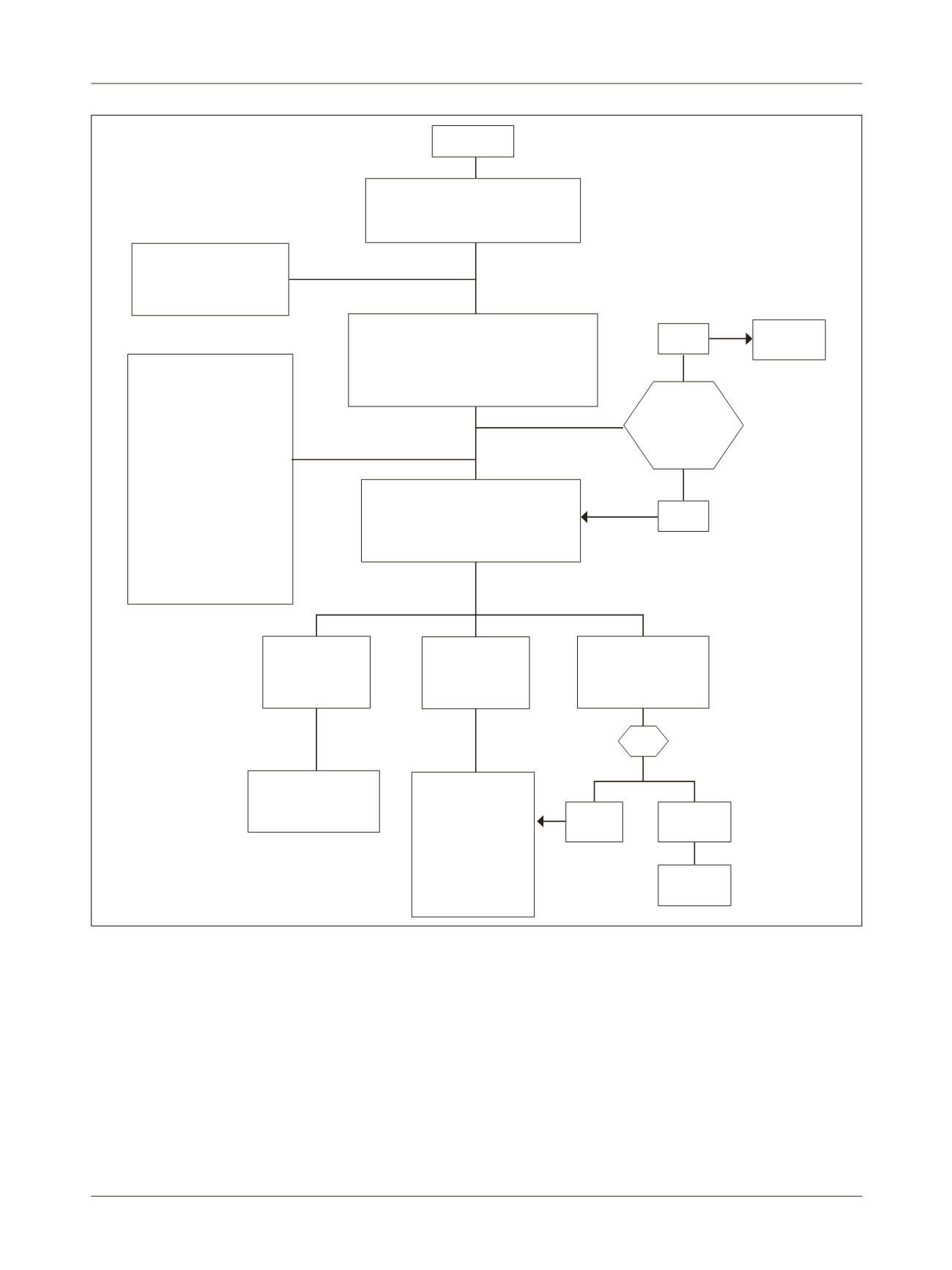
FIGURE 1
Algorithm of the initial approach to the patient in a coma.
BP: blood pressure; GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale; MAP: mean arterial pressure; HMG-CoA: 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A; GOT: glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase; GPT: glutamate-pyru-
vate transaminase; CT: computed tomography; CNS: central nervous system; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; EEG: electroencephalogram.
Yes
No
Normal
Specific
treatment
Specific
treatment
Thiamine 100 mg IV +
glucose 50%
50 mL if Dx < 60 mg/dL
Naloxone 0.4 to 2 mg IV
every 3 minutes if narcotic
poisoning is suspected
Flumazenil 0.2 mg max 1 mg
IV if poisoning by
benzodiazepines is
suspected
Gastric lavage with activated
charcoal if drug intoxication
is suspected
Intubation if GCS ≤ 8,
maintain SaO
2
> 90% and
MAP > 70 mmHg
Coma
Assessment of air ways, BP, pulse,
temperature, capillary blood glucose
Intravenous access and monitoring
Laboratory tests: HMG, Na, K, Ca, Cl, GOT,
GPT, blood gas and toxicological screening
Quick history
Brief general and neurological examination
Specific toxic-
metabolic
assessment
Thyroid hormones
Serum cortisol
Consider brain MRI,
CSF and EEG
Medical history and complete physical
examination
Head CT if structural damage or CNS
infection is suspected
CSF
Focal signs and
abnormal head
CT findings
Neurological and/or
neurosurgical
assessment
History of meningitis,
fever or meningeal
irritation
No focal signs
Normal head CT
scan
Meningitis
Evident
toxic-metabolic
cause?
that could be essential for localization and etiology of the
patient’s symptoms. Basic laboratory investigations and
imaging tests are of utmost importance for differential
diagnosis.
The prognosis is extremely variable and depends on
the cause, duration and extent of the affected site. How-
ever, effective initial care and introduction of proper treat-
ment are crucial in order to prevent the occurrence of sec-
ondary damage and to speed up patient recovery.
R
esumo
Abordagem clínica atual do paciente com distúrbios de
consciência















