C
oimbra
S
et
al
.
494
R
ev
A
ssoc
M
ed
B
ras
2014; 60(5):490-499
The assessment of the clinical status of patients invol-
ves several examinations and laboratory tests (Table 2).
When interpreting the results it is important to con-
sider that some parameters could be altered because the
monoclonal IgM may interfere in several measurements
performed in automated analyzers, especially in the eva-
luation of HDL cholesterol, bilirubin, inorganic phos-
phate, LDL cholesterol, C-reactive protein, creatinine, glu-
cose, urea, iron and calcium ions.
27
D
ifferential
diagnosis
It is fundamental to distinguish WM from other disor-
ders that could be clinically confused with this disease.
Differential diagnosis (Table 3) is important for the
exclusion of neoplasms potentially secreting monoclo-
nal IgM and which can also present lymphocytes with
lymphoplasmocytoid differentiation in the bone marrow.
This group includes marginal zone lymphomas,
57
chro-
nic lymphocytic leukemia (CD5
+
, CD23
+
), mantle cell lym-
phoma (CD5
+
, CD23
-
), follicular lymphoma (CD10
+
) and
multiple myeloma (CD138
+
, CD38
+
, CD56
+
).
17,57
The differentiation between symptomatic WM, asymp-
tomatic WM and IgM monoclonal gammopathy of un-
determined significance (MGUS) is important since the
latter patients present risk of progression to symptoma-
tic WM of 1.5%/year.
58,59
This differs from asymptomatic
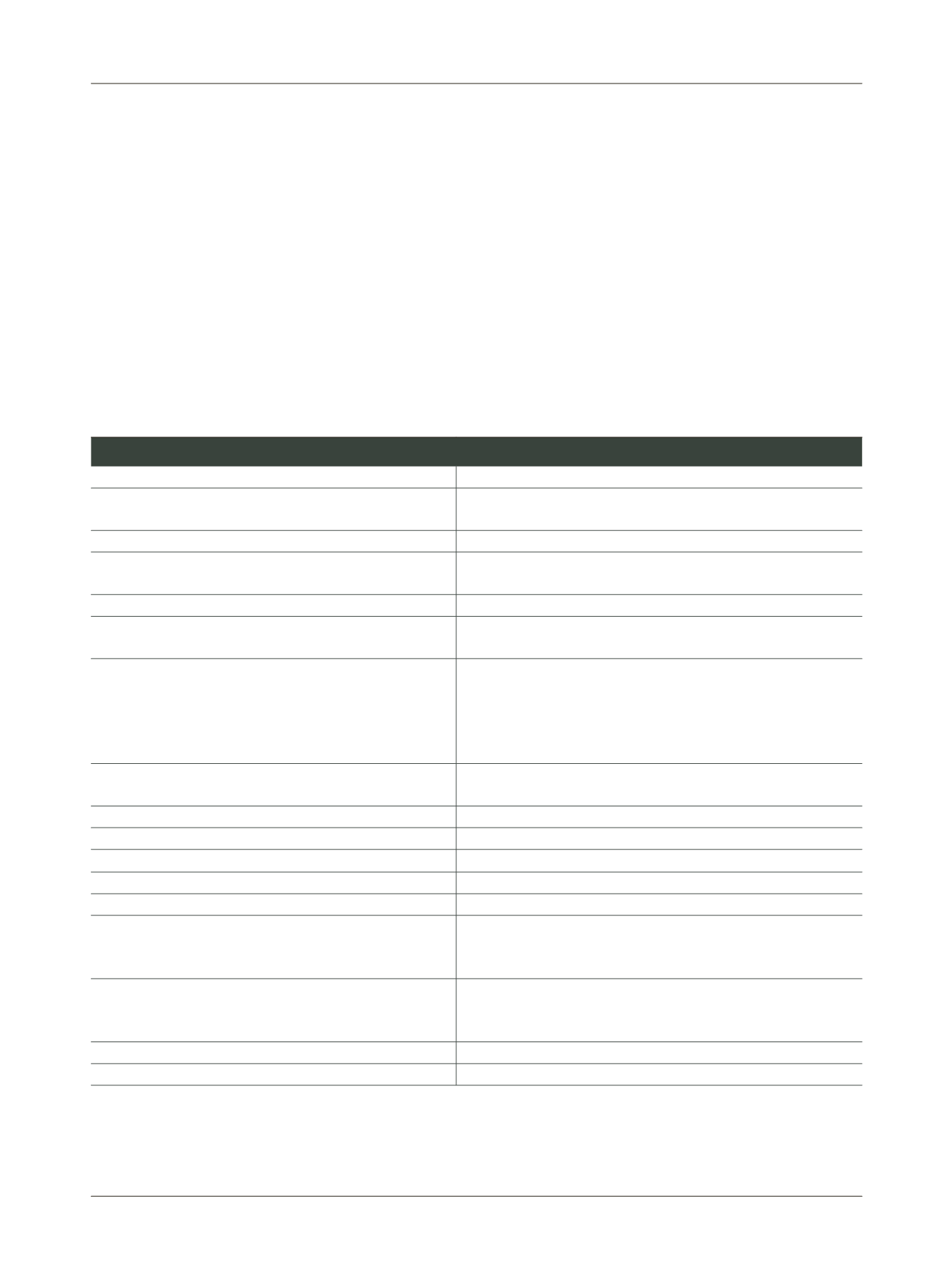
Table 2
Laboratory assessment in patients with clinical suspicion of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia
Laboratory exam
Clinical justification
Electrophoresis of serum proteins
Electrophoresis of urinary proteins (24-hour urine)
Detection of monoclonal gammopathy - homogeneous peak, high, narrow
base, usually in the area of gamma globulins
Immunofixation of serum and urinary proteins
Characterize the immunoglobulin: heavy chain and light chain
Bone marrow biopsy
Assess the bone marrow infiltration by lymphocytes, the infiltration pattern
and cell morphology
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Frequently raised
Cytogenetic studies
Differential diagnosis of other malignancies of B-lymphocytes secreting
monoclonal IgM
Blood test
- Reticulocyte count
- Concentration of haptoglobin, indirect bilirubin and lactate dehydrogenase
- Research, identification and quantification of “cold agglutinins”
- Direct Coombs Test and title of “cold agglutinins”
Evaluation of thrombocytopenia and anemia, which is usually normocytic
and normochromic
Search autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Useful in patients with Raynaud’s
syndrome, acrocyanosis or limb ulceration
Serum viscosity
Determine if the patient has signs and symptoms of hyperviscosity or IgM
concentration >4000 mg/dL
Eye examination - ophthalmoscopy
Justified in the event of changes in vision
Urea, creatinine and transaminases (AST and ALT)
Evaluation of renal and hepatic function
β
2-microglobulin
Relevant for prognosis
IgG and IgA
Predisposition to respiratory infections
TTPa, TP, TT
In patients with bleeding diathesis and a tendency to bruise
Detection and semi-quantification of anti-MAG, anti-SGPG, anti-
GM1, anti-
sulfatide
antibodies
In patients with peripheral neuropathy, such as progressive symmetrical
numbness of the limbs, burning sensation and tingling, pain in the feet and
hands
Screening of AL amyloidosis - electrophoresis and immunofixation
of urinary proteins (24-hour urine)
Confirmation of AL amyloidosis test - abdominal fat aspirate
In suspected cases of AL amyloidosis
Electromyography
In patients who have impaired motor function
Computed tomography of the abdomen, trunk and pelvis
Detection of organomegaly (e.g. spleen, liver) and lymphadenopathy
AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; PT, prothrombin time; TT, thrombin time; MAG, myelin-associated glycoprotein;
SGPG, sulfate-3-glucuronyl paragloboside; GM1, GM1 ganglioside.